The global low-code programming platform market size was valued at USD 22.25 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 28.75 billion in 2024 to USD 264.40 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 32.0% during the forecast period (2024-2032).
Together with their friends, no-code programming tools, low-code platforms threaten to significantly change the programming market. But will they replace the seasoned professionals who have been writing real code and rewriting it after their colleagues for decades? Let’s figure it out.
What is Low-Code Programming Suitable For?
Low-code and no-code platforms, or LCDP and NCDP, were developed to solve the problem of transferring correct information from a process specialist to a programmer.
In businesses, there are employees with narrow and extremely specific qualifications who deeply understand their processes and may need to automate and digitize parts of them. For example, they might need applications for data visualization or analytical dashboards that execute certain functions according to a specific algorithm. These employees often spend a significant amount of time giving tasks to programmers and then monitoring their implementation.
What is the pain?
Typically, halfway through the process, it becomes clear that programmers do not have the time for endless revisions (pushing the project to the end of the queue), and the specialists with deep expertise do not have the time to review each corrected screen twenty times (also pushing the project to the end of the queue). This communication problem stretches the task’s completion time to infinity.
At the same time, low-code and no-code platforms allow niche specialists, who are not deeply versed in programming or not familiar with it at all, to quickly create the necessary software products or elements for themselves using visual interfaces: drag-and-drop, scales and sliders, selectors, and the much-loved in many fields Excel tables. It is faster, and cheaper, and you no longer need to storm the development department.
However, the logic of low-code programming is based on the automatic generation of code based on template solutions from global practice. That is, you cannot develop something fundamentally new using low-code and no-code.
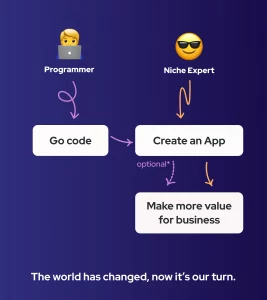
Will Low-Code Programmers Replace Classical Technicians?
No. With the help of LCDP and NCDP platforms, businesses will accelerate processes that were perpetually stalled, while the demand for programmers capable of creating projects from scratch through code will remain strong.
However, it is already noticeable that the qualifications required for such programmers are increasing. Businesses are increasingly less welcoming of the division of programmers into front-end and back-end, opting for full-stack developers who can, if not independently develop a project, then at least oversee it at all stages. Thus, we return to programming in the nineties and early 2000s: the market urgently needs deeply understanding coding specialists ready to realize any idea, and the demand for tech boomers — the generation that joined programming at its peak popularity and trained in a limited range of technologies through short courses — is unfortunately falling.
At the same time, it is expected that companies will look for niche specialists with minimal programming skills. Just as a whole generation once had to quickly master PCs to get good job positions, now niche professionals will have to get acquainted with programming useful for their field.
What Specific Business Functions Can Be Addressed with Low-Code and No-Code Programming?
Here’s another interesting question. What specific functions can businesses address using niche specialists who program without coding? There are many of these functions, and they pertain to the most vital business processes.
Workflow Automation
Low-code and no-code platforms can be used to create applications that automate repetitive tasks and processes. This includes the development of systems for task management, project tracking, and workflow automation. For instance, these platforms can help develop a tool for automatically distributing tasks among employees, monitoring deadlines, and providing status updates.
🔍 Learn how we provide this type of software development service at JetSoftPro.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Businesses can use low-code and no-code solutions to create and customize CRM systems that help manage customer interactions, track sales, manage marketing campaigns, and maintain a customer database. These systems can include features for customer segmentation, tracking preferences and interaction history, and automating email campaigns and promotions.
Data Analytics and Visualization
Low-code and no-code platforms allow the creation of powerful analytical dashboards and data visualization tools without complex programming. This is particularly useful for companies that need to process large volumes of data and present them in an easy-to-analyze format. These tools can include charts, graphs, interactive tables, and filters, enabling users to analyze data and make informed decisions quickly.
Mobile Application Development
With low-code and no-code platforms, companies can rapidly develop mobile applications for both internal and external use. This can include applications for employee management, customer interaction, inventory management, logistics, and other business functions. These applications can be integrated with existing systems and databases, ensuring seamless operation and up-to-date information.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Companies can use low-code and no-code platforms to create and customize ERP systems that help manage key business processes such as procurement, production, warehousing, logistics, and finance. These systems enable centralized management of enterprise resources, increase process transparency, and improve control over operational activities.
Customer Support and Service
Low-code and no-code platforms can be used to create customer support and service systems, including self-service portals, chatbots, and request management systems. These solutions enhance customer service quality, reduce the burden on support departments, and ensure faster and more efficient responses to customer inquiries.
So, we have entered a new stage of global business development, much more technologically advanced than all previous ones. Already, niche specialists need to understand programming at the level of low-code and no-code platforms to build their careers on automated solutions. Programmers, in turn, should delve deeper into the industry and relearn the fundamentals they neglected when they jumped into the technological niche at the height of the Great Programmer Boom.